Mazda G-Vectoring Control – How It Works
RencanaIn keeping true to their Jinba Ittai philosophy, Mazda continuously finds methods to improve the driveability of their cars. G-Vectoring Control, or GVC in short, is one of such solutions aimed to improve Mazda’s already excellent handling prowess.
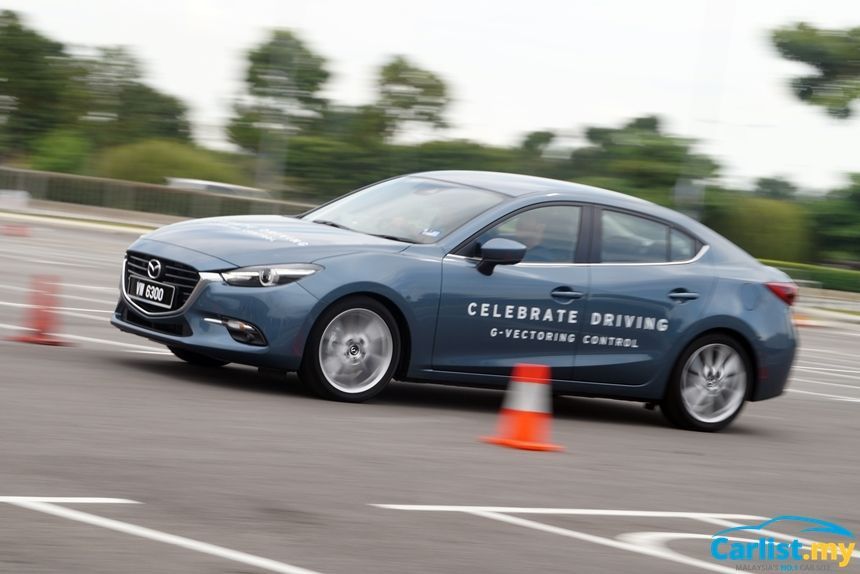

While the name seems to imply some form of torque vectoring at play, similar to what other manufacturers do, in actual fact, Mazda’s solution is far simpler.
Mazda's G-Vectoring Control monitors the steering input by the driver. As the driver turn the steering wheel, GVC controls the engine's torque to intiatiate a shift in vehicle's weight balance to shift forward. This in turn puts load on the front wheels, improving traction.
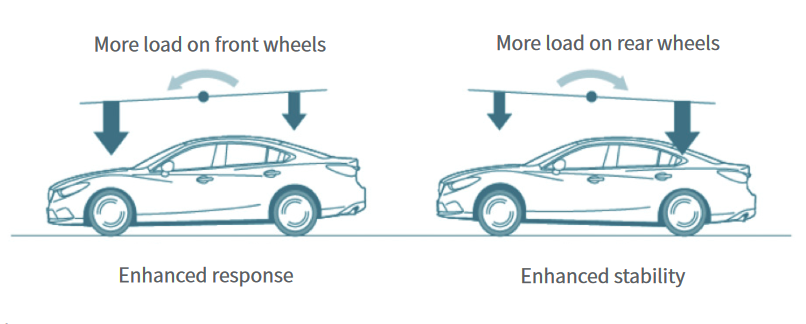
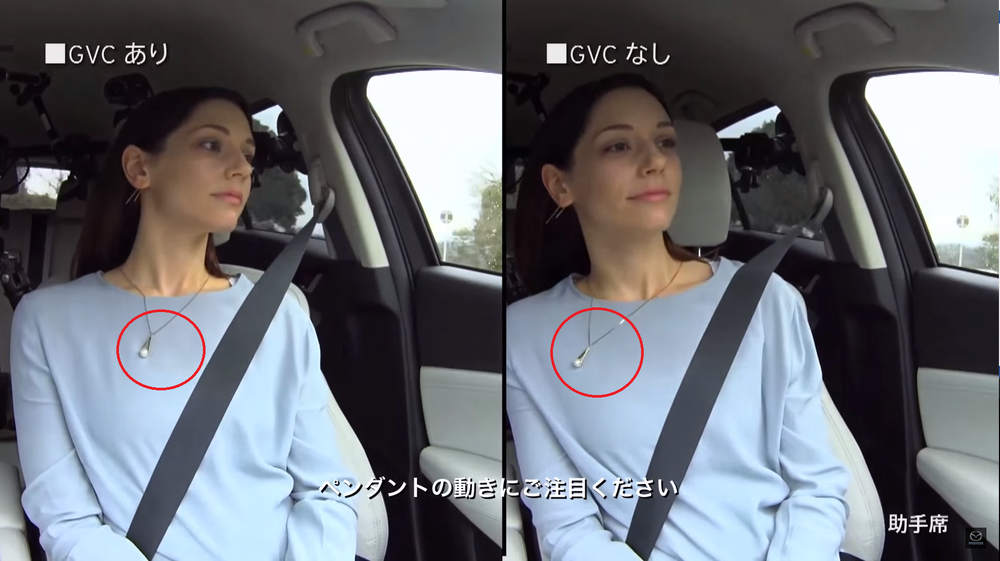
The end result is that the driver’s confidence is improved as they does not need to constantly make steering corrections, giving the driving a better sense of unity with the car. As the driver does not need to make so much steering corrections, fatigue becomes less of an issue than it was before. Last but not least, GVC also stabilizes the vehicle during an evasive maneuver, giving the occupants better sense of safety.

Currently, Bermaz offers the Mazda 2, 3, 6, CX-3, CX5 and new CX-9 with G-Vectoring Control.